5 reasons to switch to the Gradle Kotlin DSL

Gradle versions 5.0+ feature the Kotlin DSL, where you define your build script using the Kotlin language from JetBrains. Whilst the Groovy DSL is more common, there are some advantages in using Kotlin. Here are the top 5 reasons to switch to the Gradle Kotlin DSL.
1) Simplified plugins syntax
Gradle comes with built in plugins that you apply to a project by specifying the plugin id only. No version is required. Some popular examples are application, java, and jacoco.
Here's how to apply the jacoco plugin with the Gradle Groovy DSL.
plugins {
id 'jacoco'
}The Gradle Kotlin DSL has simplified syntax via property extensions for the built in plugins.
plugins {
jacoco
}An advantage of this approach is if you specify a non-existent plugin you'll get a syntax error in your IDE.
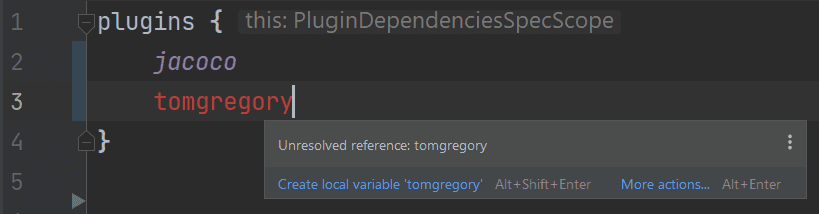
Small thing, big difference.
2) Default lazy task configuration
Configuration avoidance is a Gradle feature that improves performance by only configuring tasks that actually need to take part in the build. For example, if you execute the assemble task in a Java project, there's no need for Gradle to spend time configuring the test task.
To make full use of configuration avoidance we must ensure tasks are configured lazily.
Here's an example of non-lazy/eager task configuration with the Groovy DSL.
plugins {
id 'java'
}
tasks.jar {
archiveFileName = 'foo.jar'
}This is bad because even if we run a completely unrelated task, such as help, the jar task must be configured.
We can see the problem if we run a build scan by passing the --scan option i.e. ./gradlew help --scan. The scan result shows that 1 task was unnecessarily created during the configuration phase of the build.

Groovy DSL build scan result
The way to fix this in Groovy is to use tasks.named('jar') instead of tasks.jar to locate the task.
But in the Kotlin DSL, the same tasks.jar syntax by default uses lazy configuration.
plugins {
java
}
tasks.jar {
archiveFileName.set("foo.jar")
}This time the build scan shows that no tasks were created during the configuration phase. Much better!

Kotlin DSL build scan result
So using the Gradle Kotlin DSL promotes good practice by automatically setting up task configuration avoidance.
3) Compile time checks
Groovy is a dynamic language, so when working with the Groovy DSL you get the impression that there's a lot of unexplained magic going on. ✨
Kotlin on the other hand is a statically typed language. Build script errors tend to surface during compilation rather than execution.
Let's take this example, which has a deliberate error since we're referencing the configuration name jacocos instead of jacoco.
plugins {
id 'jacoco'
}
println 'Configuring Jacoco'
jacocos {
toolVersion = "0.8.1"
}When we run ./gradlew help we see the error is only detected while executing the build script. We know this because the Configuring Jacoco string is printed.
$ ./gradlew help
> Configure project :
Configuring Jacoco
FAILURE: Build failed with an exception.Here's the same setup within the Kotlin DSL.
plugins {
jacoco
}
println("Configuring Jacoco")
jacocos {
toolVersion = "0.8.1"
}Running ./gradlew help results in a compilation error before the script was even executed.
$ ./gradlew help
> Configure project :
e: C:\workspace\gradle-tutorials-kotlin\task-inputs-and-outputs\custom-task\build.gradle.kts:6:1: Unresolved reference: jacocos
e: C:\workspace\gradle-tutorials-kotlin\task-inputs-and-outputs\custom-task\build.gradle.kts:7:5: Unresolved reference: toolVersion
FAILURE: Build failed with an exception.Compile time errors are a lot more useful than runtime errors, as they give you a chance to fix the problem earlier. If you're working within an IDE, you'll even get the error highlighted in your editor.
4) Better IDE experience
IntelliJ IDEA provides the most integrated experience for Kotlin, with code completion, navigation to sources, and refactoring.
| Build import | Syntax highlighting | Semantic editor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IntelliJ IDEA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Android Studio | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Eclipse | ✓ | ✓ | ✖ |
| Visual Studio Code | ✓ | ✓ | ✖ |
Gradle Kotlin DSL IDE support as per documentation
If you're using IntelliJ IDEA, when configuring plugins or tasks it's a lot easier with the Kotlin DSL. You get suggestions of what properties you can configure by hitting Ctrl + Space.

You get no such autocompletion when using the Groovy DSL.
We also saw earlier that as a result of the Kotlin DSL compile time checks, it's easier to see mistakes in the IDE.
Another win for Kotlin then, assuming you're using IntelliJ IDEA.
5) It's Kotlin!
From first impressions Kotlin seems to be a nicer language to work with than Groovy, especially coming from a Java background.
Here are 3 features that might make you sigh with relief.
Only one type of string
With Groovy, strings can be defined using the single quote 'abc' or double quote "abc" syntax. The latter is used when you want to do variable substitution within the string.
This leads to confusion within a Gradle build script, since you have to decide which type of string to use. This can lead to inconsistencies.
plugins {
id 'jacoco'
id "java"
}Kotlin does away with this and only has the double quote syntax "abc". Single quotes are used for characters, just like in Java. Phew!
Null safe
Java allows variables to be assigned null, causing potential NullPointerException scenarios that we don't find out about until it's too late. 💣
In Kotlin, by default variables cannot be assigned the null value.
var a: String = "abc" // Regular initialization means non-null by default
a = null // compilation errorIf you want variables to be nullable, you have to explicitly define them that way. In the above example, that would be using String? instead of String.
Even if a variable is nullable, Kotlin still has compile time checks to make sure that anywhere you're accessing the variable you're doing appropriate null value checks. If you're not, the code won't compile. Very cool!
To read more, check out the Kotlin null safety documentation, from which the above code snippet was taken.
Statically typed
Did I already mention this? It's so good it's worth saying again. In Kotlin, as opposed to Groovy, variables must be given a specific type.
It's clever about figuring out the type automatically.
val a: Int = 1 // immediate assignment
val b = 2 // \`Int\` type is inferred
val c: Int // Type required when no initializer is provided
c = 3 // deferred assignmentFrom experience dynamic types introduce a lot of ambiguity into a codebase. Less ambiguity means less chance of error.
For more info, check out the Kotlin basic syntax documentation, where the above snippet was found.
Conclusion
Are you already convinced to migrate your Gradle project to the Kotlin DSL? If so, check out Gradle's article Migrating build logic from Groovy to Kotlin which should help you get started.
Watch this video demonstrating the ideas from this article.
Lack of Gradle knowledge slowing you down?
A broken build is easy enough to fix. But a misconfigured build is the silent time killer that costs hours every week.
Slow builds. Slow tests. Slow development.
But the official Gradle docs are confusing. Most developers never properly configure their projects—and as codebases grow, builds become bottlenecks.

This guide fixes that. It's a step-by-step walkthrough for Java developers who want to master Gradle fast.
- Unlock the mysteries of the build script.
- Speed up your workflow.
- Make development fun again.
If this is a problem you're dealing with in your own team, you can see how I approach software delivery in practice.